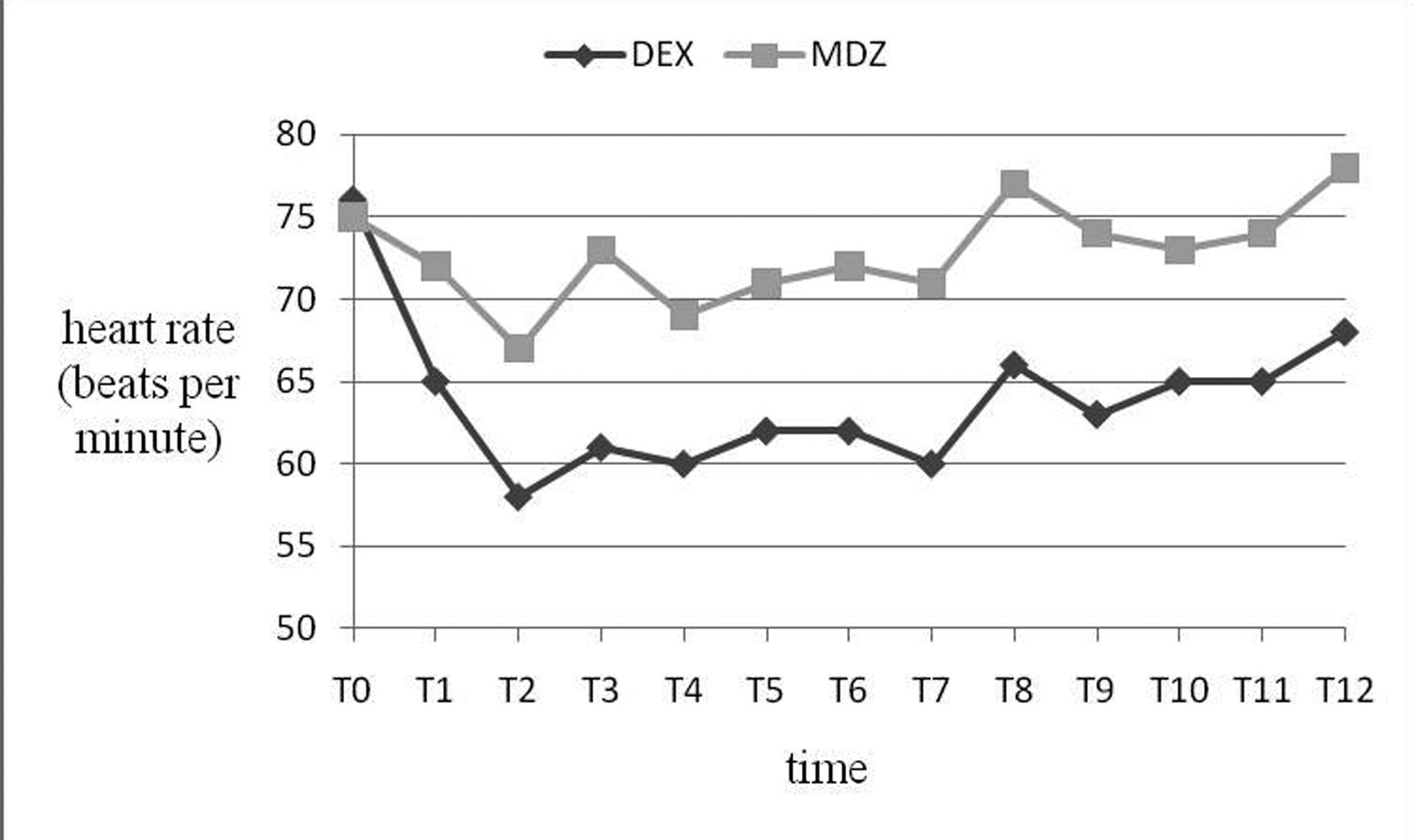
Figure 1. Heart rate (HR, beats/min) variables during study drug infusion (T0-T7), the end of surgical procedures (T8), recovery period (T9-T12). HR in group DEX was significantly lower than Group MDZ ((P < 0.001). The time scale is not linear.
| Journal of Current Surgery, ISSN 1927-1298 print, 1927-1301 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Curr Surg and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.currentsurgery.org |
Original Article
Volume 1, Number 1, December 2011, pages 12-18
A Comparison of Dexmedetomidine and Midazolam for Sedation in Gynecologic Surgery Under Epidural Anesthesia
Figures

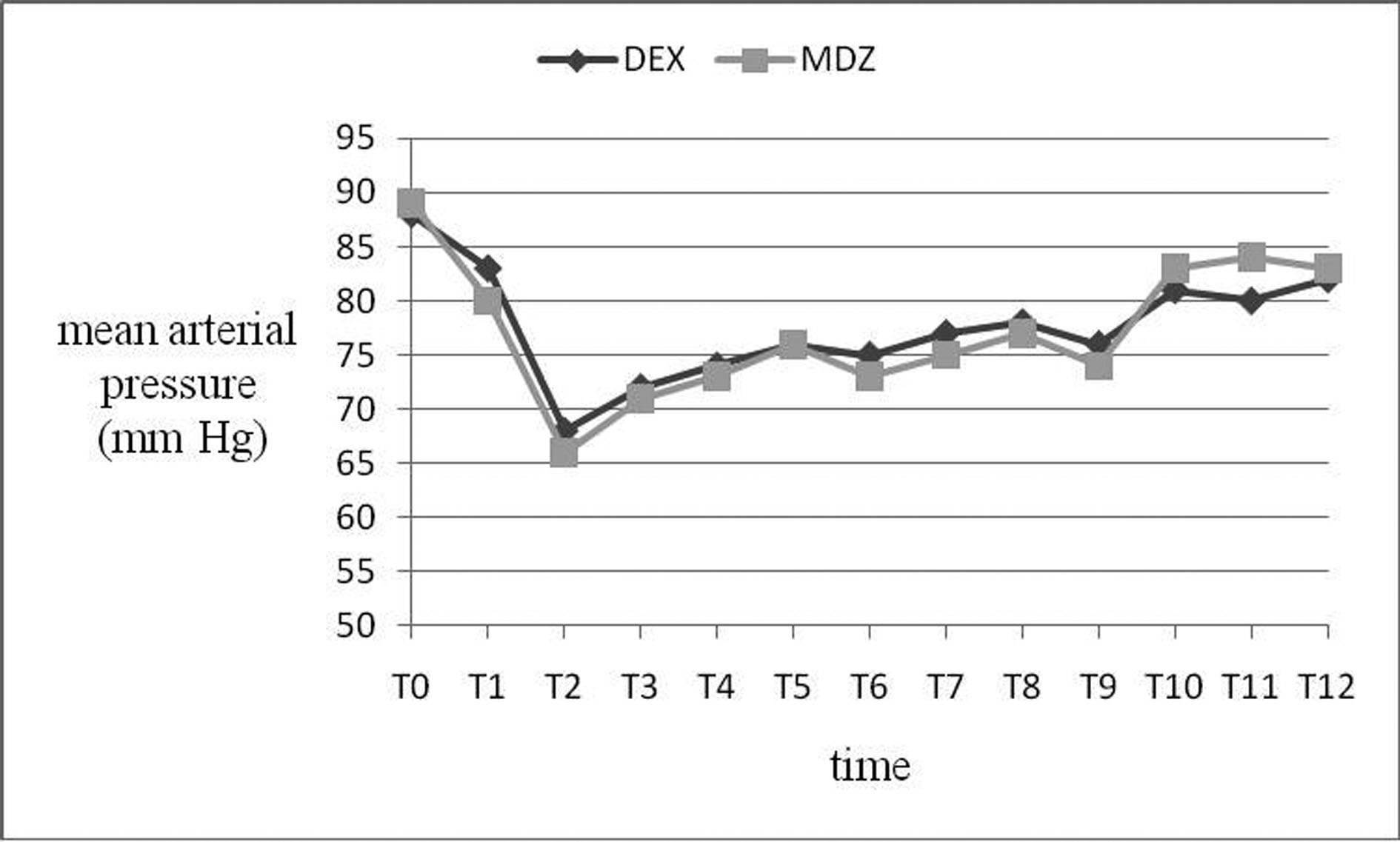
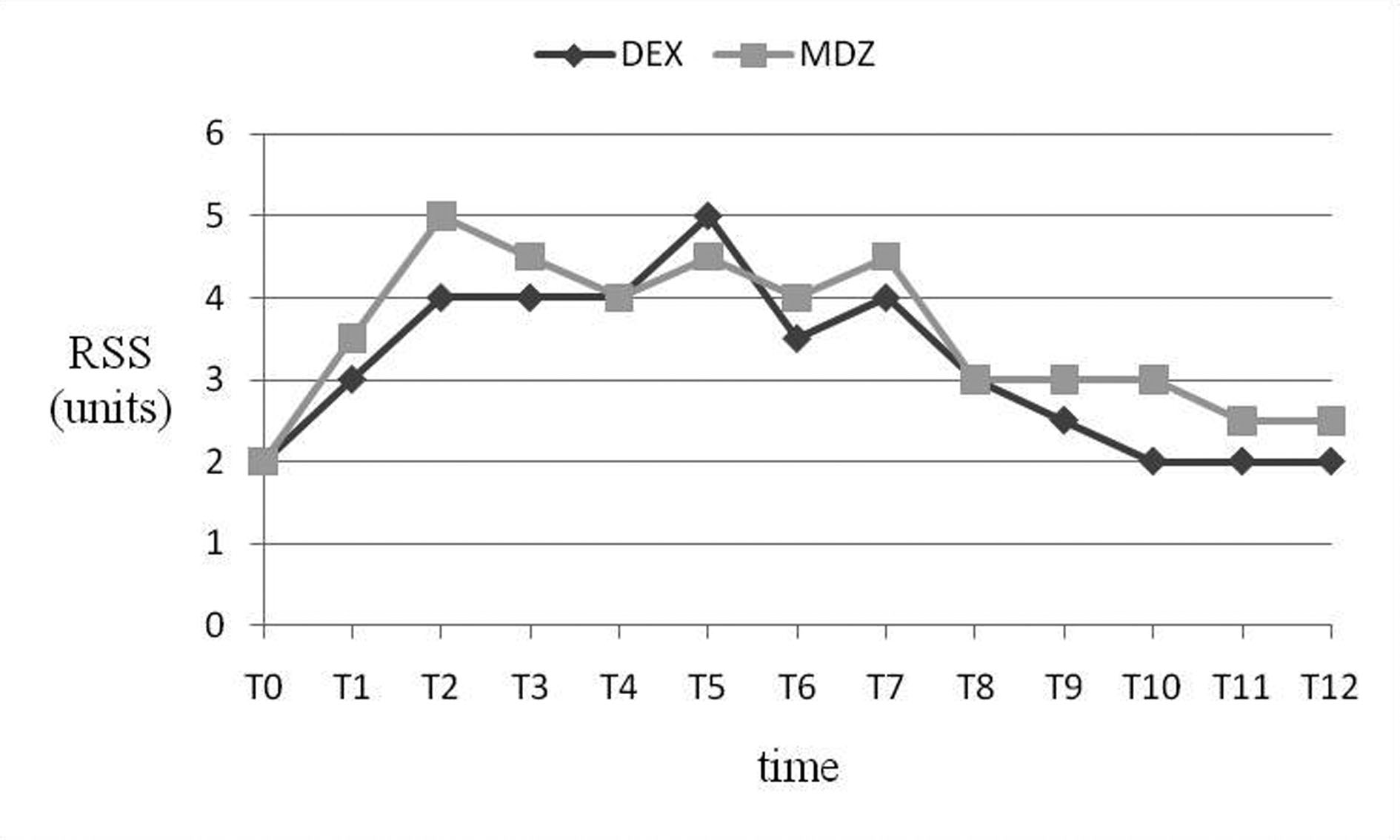
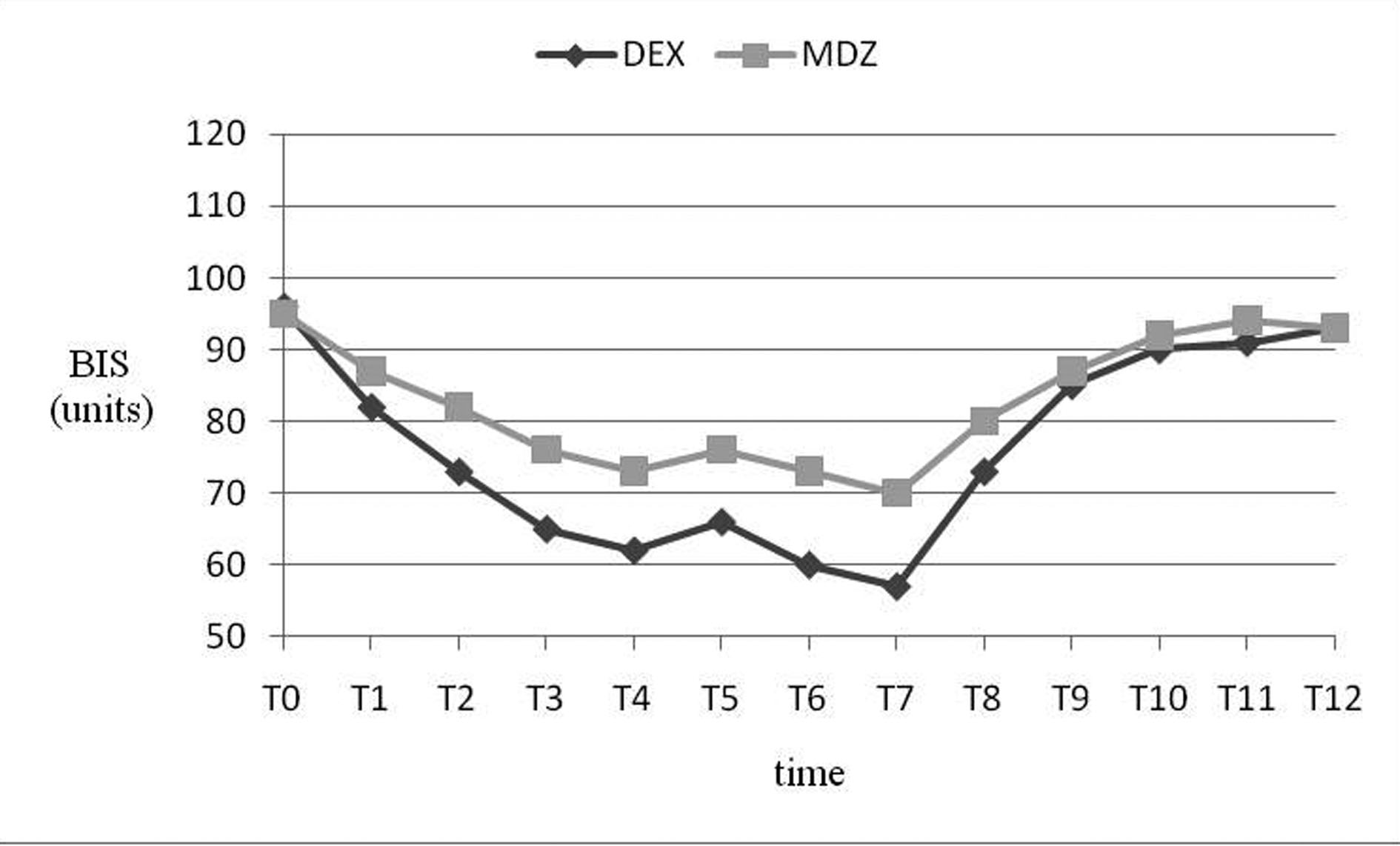
Table
| Variable | MDZ group (n = 63) | DEX group (n = 61) | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data are given as mean ± standard deviation or as percentage. | |||
| Age (y) | 50 ± 6 | 49 ± 4 | 0.391 |
| Weight (kg) | 68 ± 3 | 67 ± 8 | 0.947 |
| ASA Grade | |||
| 1 | 52 (97%) | 53 (97%) | 0.504 |
| 2 | 11 (3%) | 8 (3%) | |
| RASS of three or above (n, %) | 61 (97%) | 61 (100%) | 0.162 |
| Operative time (min) | 101 ± 30 | 102 ± 41 | 0.879 |
| Total fentanyl dose (mg) | 54 ± 11 | 17 ± 7 | 0.016 |
| Bradycardia (n, %) | 3 | 11 | 0.020 |
| Hypotension (n, %) | 10 | 8 | 0.664 |
| Respiratory depression (n, %) | 8 | 0 | 0.004 |
| Recovery time (min) | 45 ± 8 | 42 ± 5 | 0.495 |
| Mean patients’ satisfaction score | 8 | 9 | 0.779 |
| Mean surgeons’ satisfaction score | 9 | 9 | 0.834 |