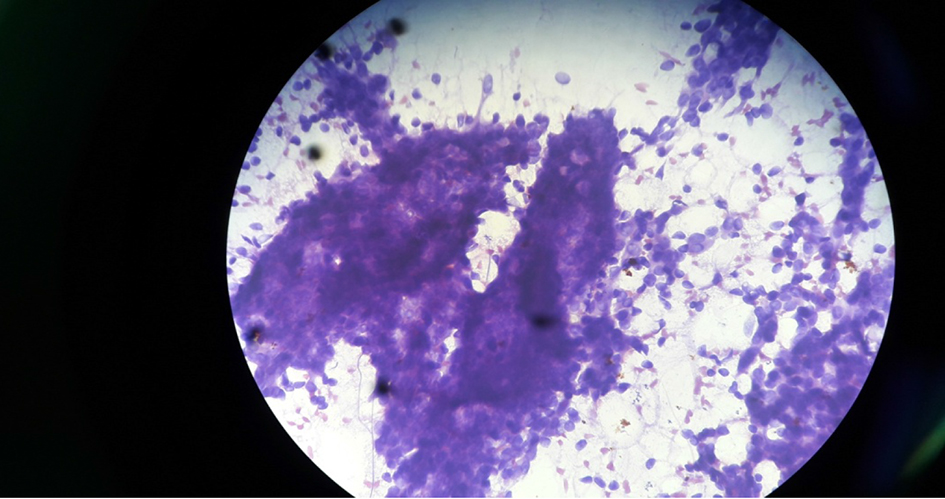
Figure 1. Cytology of fibroadenoma under microscope (× 40 objective).
| Journal of Current Surgery, ISSN 1927-1298 print, 1927-1301 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Curr Surg and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.currentsurgery.org |
Original Article
Volume 8, Number 3-4, November 2018, pages 27-31
A Clinicopathologic Study of Various Breast Lesions by Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC)
Figures

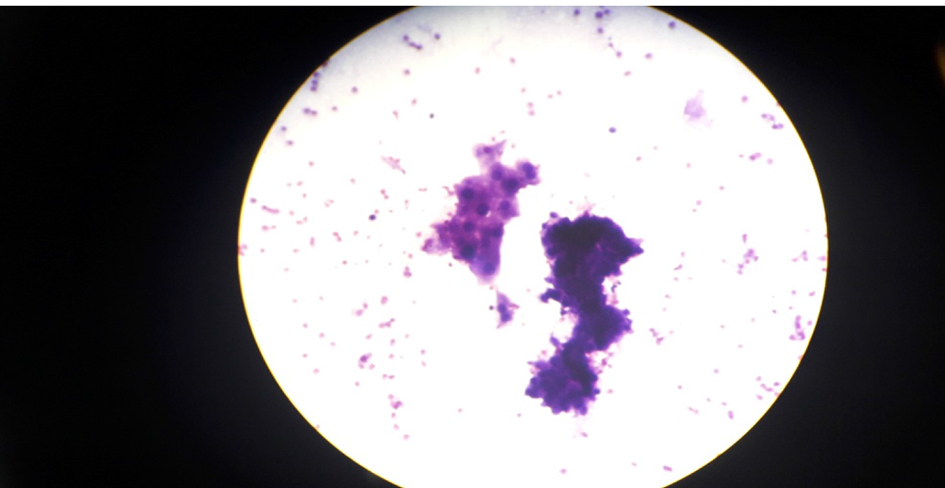
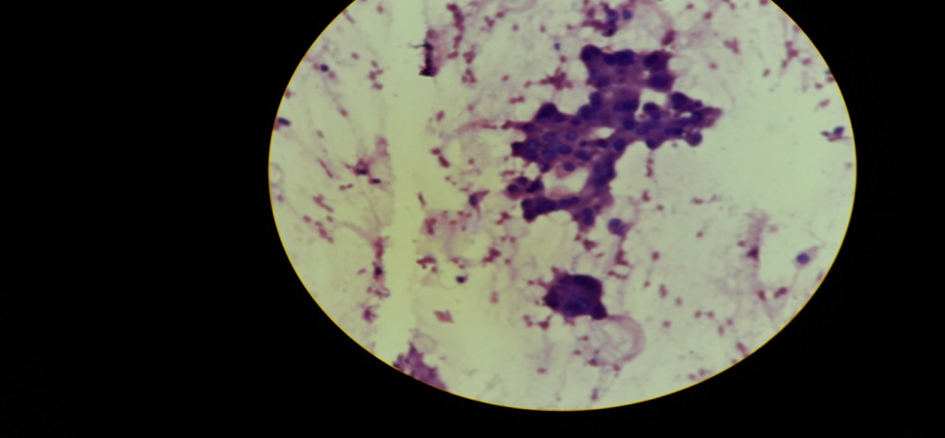
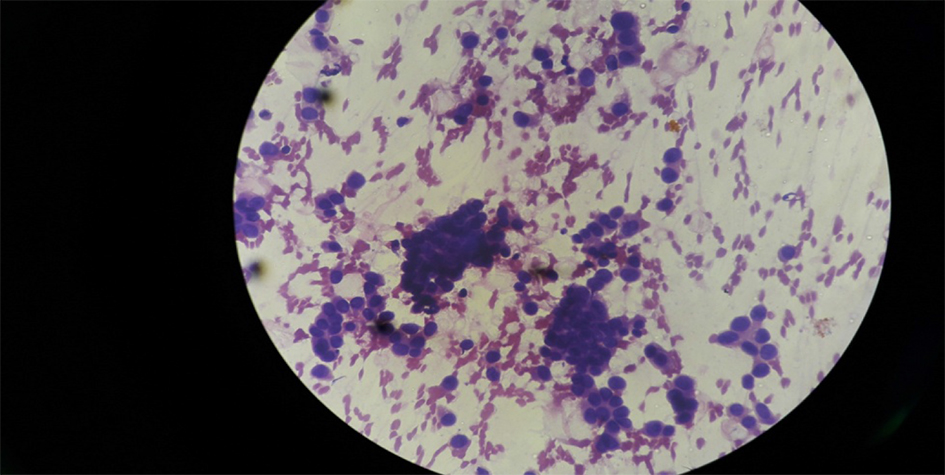
Tables
| Age (years) | Total number of cases and percentage (%) (n = 50) | Benign cases (%) (n = 43) | Malignant cases (%) (n = 07) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 - 20 | 18 (36%) | 18 (41.8%) | 0 (0%) |
| 21 - 30 | 15 (30%) | 14 (32.6%) | 1 (14.3%) |
| 31 - 40 | 5 (10%) | 5 (11.6%) | 0 (0%) |
| 41 - 50 | 8 (16%) | 4 (9.4%) | 4 (57.1%) |
| 51 - 60 | 4 (8%) | 2 (4.6%) | 2 (28.6%) |
| Total | 50 (100%) | 43 (100%) | 07 (100%) |
| Max dimension (cm) | Number of breast lump | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | Malignant | Total | |
| ≤ 1 cm | 7 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 7 |
| 1.1 - ≤ 2 cm | 16 (94.1%) | 1 (5.89%) | 17 |
| 2.1 - ≤ 3 cm | 14 (73.68%) | 5 (26.32%) | 19 |
| 3.1 - ≤ 4 cm | 3 (75%) | 1 (25%) | 4 |
| ≥ 4.1 cm | 3 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 3 |
| Quadrant | Number of cases (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Right | Left | Total | |
| Upper-outer | 13 | 11 | 24 (48%) |
| Lower-outer | 2 | 0 | 2 (4%) |
| Sub-areolar | 6 | 5 | 11 (22%) |
| Upper-inner | 6 | 4 | 10 (20%) |
| Lower-inner | 2 | 1 | 3 (6%) |
| Total | 29 (58%) | 21 (42%) | 50 (100%) |
| Cytological diagnosis | No. of cases | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Fibroadenoma | 17 | 39.54% |
| Fibrocystic change/other cystic lesion | 12 | 27.9% |
| Inflammatory/mastitis/abscess | 8 | 18.6% |
| Lactational change/galactocele | 4 | 9.3% |
| Gynecomastia | 1 | 2.33% |
| Benign phyllodes | 1 | 2.33% |
| Total | 43 | 100% |