| Journal of Current Surgery, ISSN 1927-1298 print, 1927-1301 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Curr Surg and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.currentsurgery.org |
Case Report
Volume 4, Number 2, June 2014, pages 49-51
The Sternalis Muscle: An Unusual Anatomic Finding During Reconstruction of the Soft Tissue Defect of Mouth Floor and Neck, A Case Report
Elif Saria, e, Huseyin Fatih Oktemb, Mustafa Durgunc, Hulda Rifat Ozakpinarb, Ali Teoman Tellioglud
aPlastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery Department, Kirikkale University Faculty of Medicine, Turkey
bPlastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery Clinic, Diskapi Yildirim Beyazit Education and Research Hospital, Turkey
cPlastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery Department, Dicle University Faculty of Medicine, Turkey
dPlastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery Department, Yildirim Beyazit University Faculty of Medicine, Turkey
eCorresponding author: Elif Sari, Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery Department, Kirikkale University Faculty of Medicine,Yahsihan, Kirikkale, Turkey
Manuscript accepted for publication February 19, 2014
Short title: Rectus Sternalis Muscle
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jcs221w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
The sternalis muscle is a rare anatomic structure that lies superficial to the sternum. Here we report a 50-year-old male patient that has left sternalis muscle. We met the sternalis muscle while we were performing the reconstruction of soft tissue defect of neck and mouth floor. Thus, we elevated the pectoralis major muscle with sternalis muscle simultaneously for covering the defect. We had not known about sternalis muscle, before we came across it during the pectoralis major flap elevation to cover the soft tissue defect of the neck and mouth floor in a patient. So we decided to share this case with you for its usefulness at plastic surgery practice.
Keywords: Sternalis muscle; Mouth floor defect; Reconstruction
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Sternalis muscle is a flat, accessory muscle that lies superficially at sternal area. It is an accessory muscle that settles on the surface of the sternum and the sternocostal part of the pectoralis muscle. Its reported incidence is about 4% to 7% in white, 8.4% in black and 11.5% in Asian populations, showing more prevalence in the Asian community [1]. Though it was described three centuries ago, the origin of the muscle is not still detected. Some authors reported that it originates from adjacent muscles such as the sternocleidomastoid muscle, pectoralis major muscle, rectus abdominis muscle, remnant of panniculus carnosus, and so on. In this report, we presented a case that we have detected sternal muscle during the reconstruction of soft tissue defect of the mouth floor and neck.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
A 50-year-old male patient was taken to our clinic with neck and mouth floor defect due to larynx carcinoma operation (Fig. 1). The left pectoralis major muscle flap was planned for covering the soft tissue defect. When the pectoralis major muscle was elevated, an unusual anatomic muscle structure was determined neighborly to the sternum. It was extending from the second intercostal space to the lower end of the sternum (Fig. 2). We elevated the pectoralis major muscle with rectus sternalis muscle together for reconstruction of the soft tissue defect of neck and mouth floor. No complication was observed during and after operation (Fig. 3).
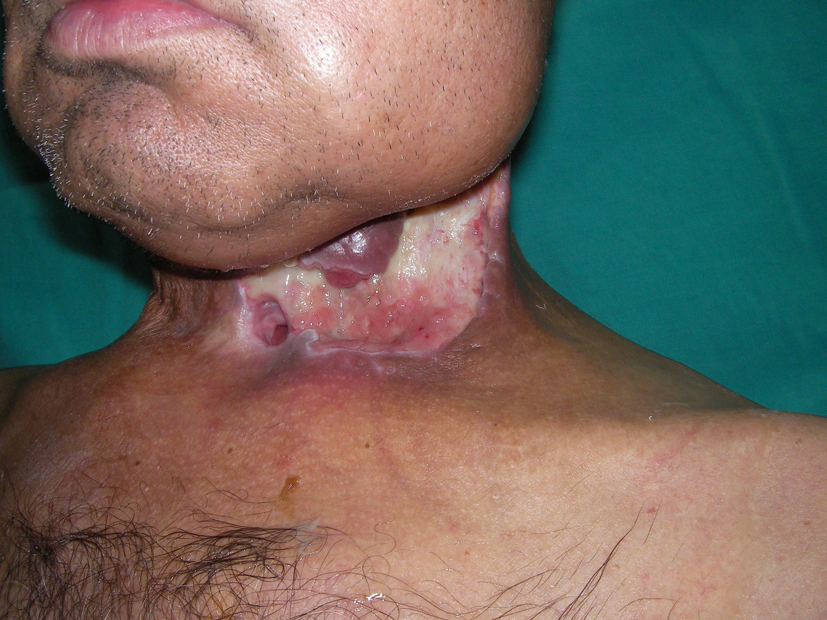 Click for large image | Figure 1. Preoperative view of the defect. |
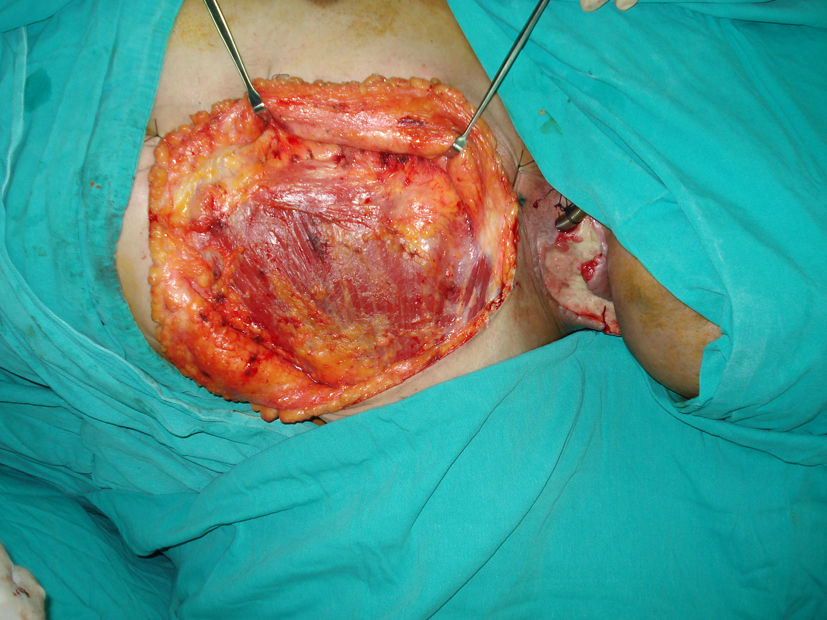 Click for large image | Figure 2. Intraoperative picture of rectus sternalis muscle. |
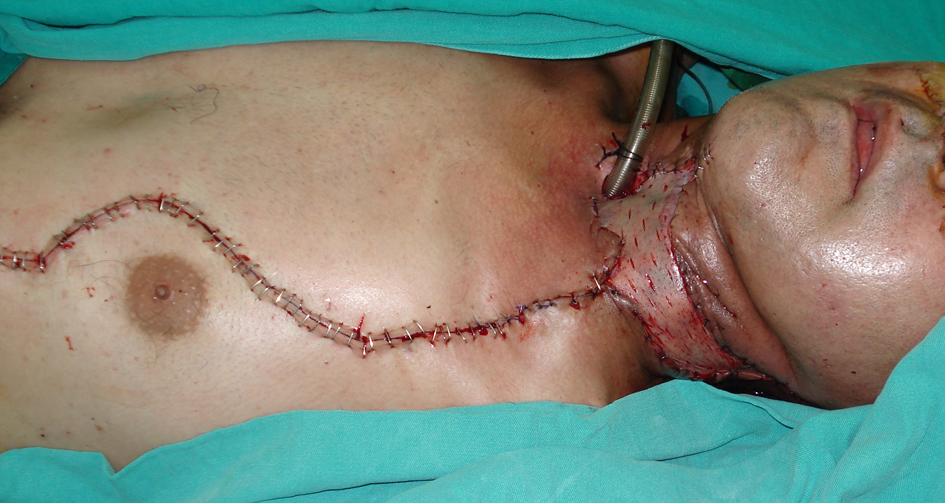 Click for large image | Figure 3. Closure of the defect with pectoralis major and rectus sternalis muscle flap and split thickness skin graft. |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
A relatively unknown muscle rectus sternalis is non-mentioned anatomic structure during medical training and also there is not any information about this muscle at standard medical books [2]. The sternalis can be unilateral or bilateral. It lies between the pectoralis major and the superficial fascia. The muscle is about 12 to 15 cm long and runs parallel to the sternum. The distance between the two sternal muscles is about 3.5 cm [3]. The intercostals or pectoral nerves innervate the muscle.
Other chest anomalies can accompany with this unknown muscle [4]. Because of its particular location, it has been suggested that contraction of the sternalis muscle can elevate the lower part of the chest. Thus, it is an accessory muscle, which may suggest the hernia of the pectoralis muscle [5, 6]. Bradley et al discover this muscle in only four of 32,000 patients [7]. Also it can create variety on the electrocardiogram or occasionally be misdiagnosed as a pathologic bulk requiring surgical resection [6, 8].
Presence of rectus sternalis may interfere with the submuscular pocket dissection when an intraalveolar or submammary approach is used and it can be used to cover the prosthesis in its most medical part and can be used for reconstruction surgery after mastectomy [9, 10]. We used this extreme muscle for reconstruction of the defect of mouth floor and neck with pectoralis major muscle. If we had known rectus muscle’s anatomy and vascular supply, perhaps we did not use pectoralis muscle for reconstruction. Therefore we used the two muscles together. And we did not see any complication during surgery and postoperative period.
Eventually this rare muscle can be useful for plastic surgeon for reconstruction of the adjacent defects. Also the distribution of vascular pattern of the muscle might be important for using it as a free flap. It is a thin and flat muscle that is suitable for covering the shallow defects. So, if we can detect this muscle before the reconstruction of a defect radiographically, the muscle can be elevated for the closure. And because of its accessory function, the patient will not lose physical capacity. We think that further studies about rectus sternalis will be effective for plastic surgeons.
Acknowledgments
Authors declare that they did not use any financial support and sponsor in this study.
Conflict of Interest
All authors disclose that they have not gotten any financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence (bias) their work.
| References | ▴Top |
- Bergman RA, Afifi AK, Miyauchi R. Illustrated encyclopaedia of human anatomic variation: Part I. University of Iowa. Virtual Hospital. 2001.
- Bailey PM, Tzarnas CD. The sternalis muscle: a normal finding encountered during breast surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999;103(4):1189-1190.
doi - Jelev L, Georgiev G, Surchev L. The sternalis muscle in the Bulgarian population: classification of sternales. J Anat. 2001;199(Pt 3):359-363.
doi pubmed - Das S, Paul S, Mandal AK. Anomalous musculoskeletalmorphology of anterior chest wall: A case report. Arch Med Sci. 2006;4:289-291.
- Jeng H, Su SJ. The sternalis muscle: an uncommon anatomical variant among Taiwanese. J Anat. 1998;193(Pt 2):287-288.
doi pubmed - Pereira BDV, Tavares AS. Sobre um caso de coexistencia do musculo pre-esternal e de arco axilar muscular. Clinica Contemporanea. 1946;9:526-528.
- Bradley FM, Hoover HC, Jr., Hulka CA, Whitman GJ, McCarthy KA, Hall DA, Moore R, et al. The sternalis muscle: an unusual normal finding seen on mammography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;166(1):33-36.
doi pubmed - Glasser SP. Electrocardiogram of the month. J La State Med Soc. 1975;127(4):136, 149.
- Khan UD. Use of the rectus sternalis in augmentation mammoplasty: case report and literature search. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2008;32(1):21-24.
doi pubmed - Schulman MR, Chun JK. The conjoined sternalis-pectoralis muscle flap in immediate tissue expander reconstruction after mastectomy. Ann Plast Surg. 2005;55(6):672-675.
doi
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Current Surgery is published by Elmer Press Inc.
