| Journal of Current Surgery, ISSN 1927-1298 print, 1927-1301 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Curr Surg and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.currentsurgery.org |
Case Report
Volume 11, Number 4, December 2021, pages 97-100
Complex de Garengeot’s Hernia With a Bladder Diverticulum
Marco De Montia, b , Alessandro Torrea, Laura Ossolaa, Luca Reguscia
aDepartment of Surgery, EOC Ente Ospedaliero Cantonale - “Beata Vergine” Regional Hospital of Mendrisio, Mendrisio, Switzerland
bCorresponding Author: Marco De Monti, Department of Surgery, EOC Beata Vergine Regional Hospital, Via Turconi 23, CH 6850 Mendrisio, Switzerland
Manuscript submitted October 26, 2021, accepted November 16, 2021, published online December 31, 2021
Short title: Complex de Garengeot’s Hernia
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jcs451
| Abstract | ▴Top |
De Garengeot’s hernia is a type of femoral hernia that also contains the appendix. It is a rare phenomenon and is diagnosed usually intraoperatively, during surgery aimed at reducing and repairing the symptomatic femoral hernia. In some cases the development of appendicitis can further complicate the clinical presentation. This paper presents a recent case of an incarcerated de Garengeot’s hernia containing both the cecal appendix and a voluminous bladder diverticulum. The purpose of this article is to highlight the importance of differential diagnosis in patients with a groin mass. The ability to correctly identify hernial content preoperatively can, in fact, modify the surgical approach taken and allow the operation to be performed more safely. There are currently no specific guidelines for its treatment, as there is no statistical evidence on the best management approaches and their outcomes. The authors of this paper present an ideal flow chart on how to deal with this particular type of hernia safely and effectively.
Keywords: Garengeot; Femoral hernia; Bladder diverticulum; Appendix herniation
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Abdominal wall hernias have a range of different names and how they vary in clinical presentation can create further confusion regarding their nomenclature. The de Garengeot’s hernia is often confused with the more well-known Amyand hernia described by Claudius Amyand in 1735 in which the appendix is found inside an inguinal hernia [1]. Appendicular herniation within a femoral hernia, on the other hand, was described for the first time in 1731 by the French surgeon Rene Jacques Croissant de Garengeot and hence its current eponym [2]. Our interest was raised in this particular type of hernia when a female patient was presented to our observation with a painful groin mass, which turned out to be a de Garengeot’s hernia containing both an inflamed appendix and a bladder diverticulum.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
Investigations
A 90-year-old female patient came to the hospital reporting the appearance of a painful groin mass at the right groin femoral level several days ago. The patient also presented with non-symptomatic umbilical and epigastric hernias. She denied nausea and vomiting, had no urinary symptoms and defecation was regular. She had not undergone any previous abdominal surgery. On physical examination, a non-reducible right femoral hernia was discovered.
Laboratory results showed a slightly increased C-reactive protein of 59 mg/L (normal value: < 5 mg/L) and a normal white blood cell count of 7.0 × 109/L (normal value: 4.0 - 10.0 × 109/L).
An abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan with contrast media allowed us to identify the presence of a right femoral hernia of approximately 5 cm with sign due to a concomitant inflammatory process.
The CT scan also revealed the presence of liquid effusion and an inflamed cecal appendix with thickened walls in the hernial sac (Figs. 1, 2), as well as a bulky herniated bladder diverticulum causing the stretching of the right lateral inferior bladder wall (Figs. 3, 4).
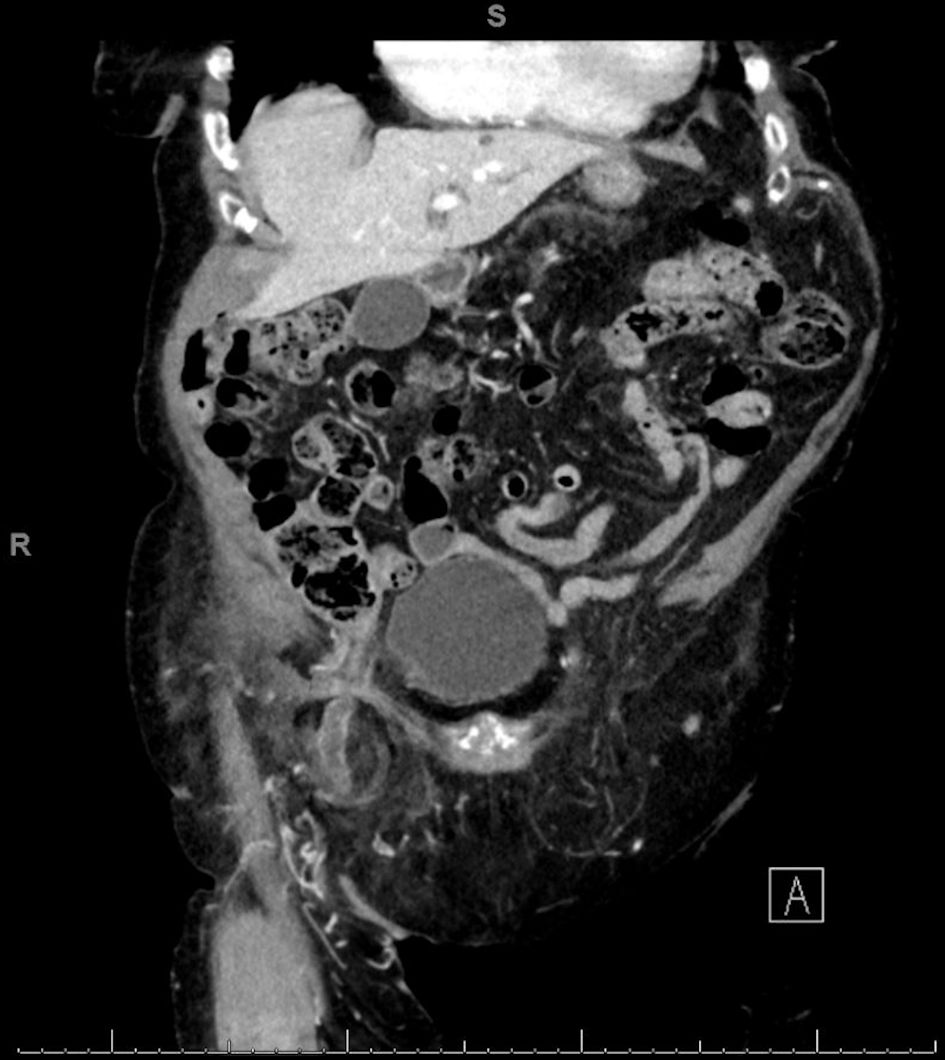 Click for large image | Figure 1. CT coronal scan: right femoral hernia containing liquid effusion and an inflamed cecal appendix. CT: computed tomography. |
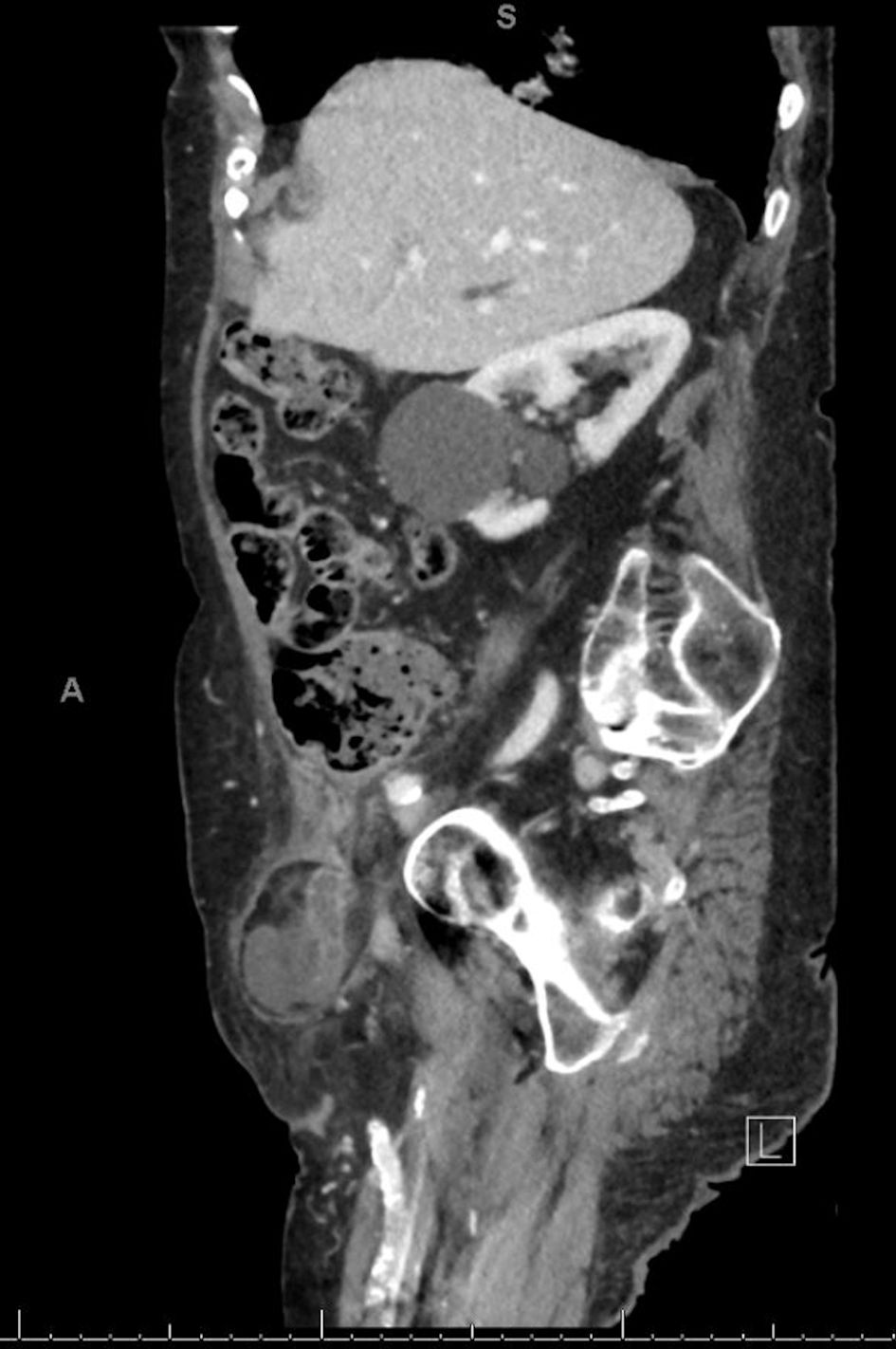 Click for large image | Figure 2. CT sagittal scan: right femoral hernia containing an inflamed cecal appendix. CT: computed tomography. |
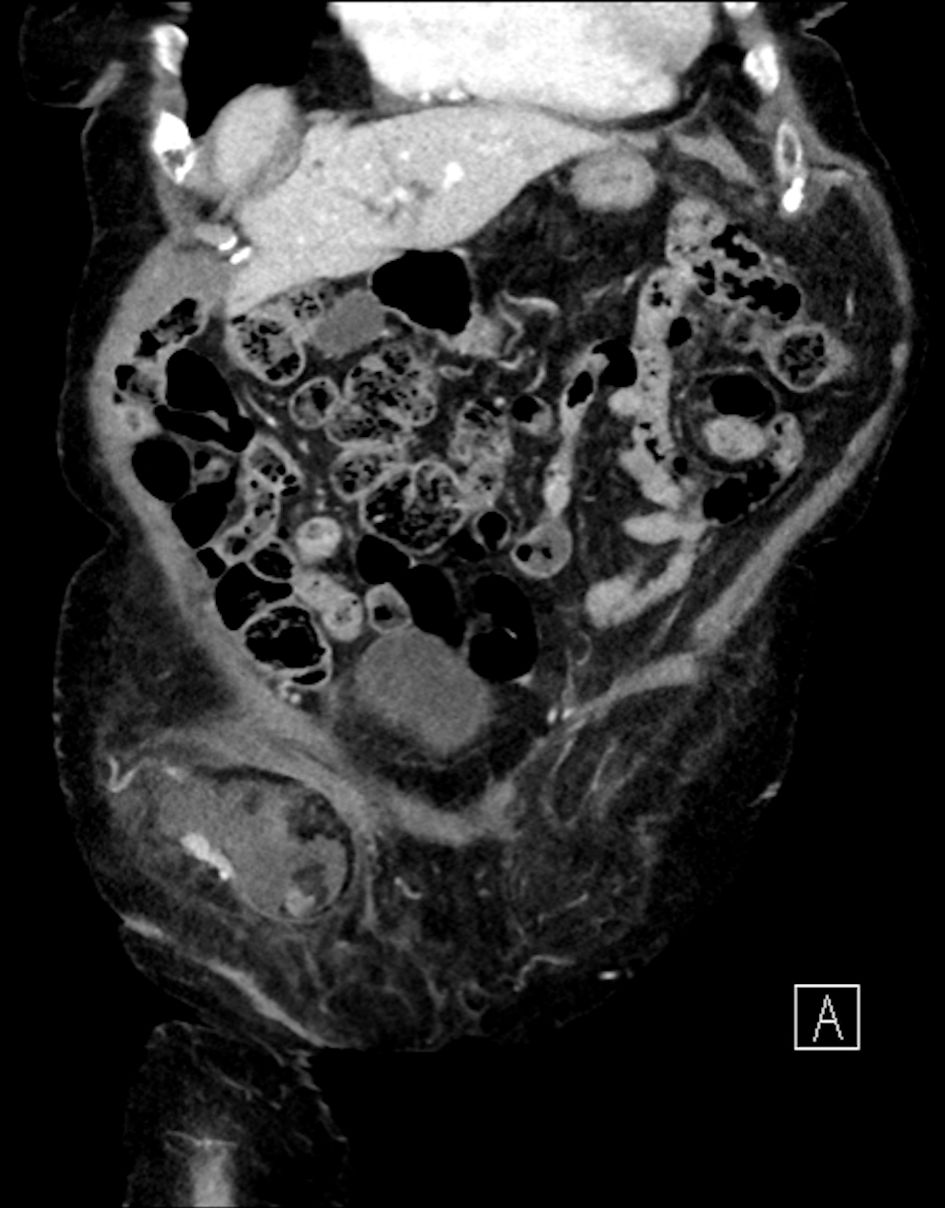 Click for large image | Figure 3. CT coronal scan: right femoral hernia containing a bulky bladder diverticulum of approximately 5 cm, causing the stretching of the right lateral inferior bladder wall. CT: computed tomography. |
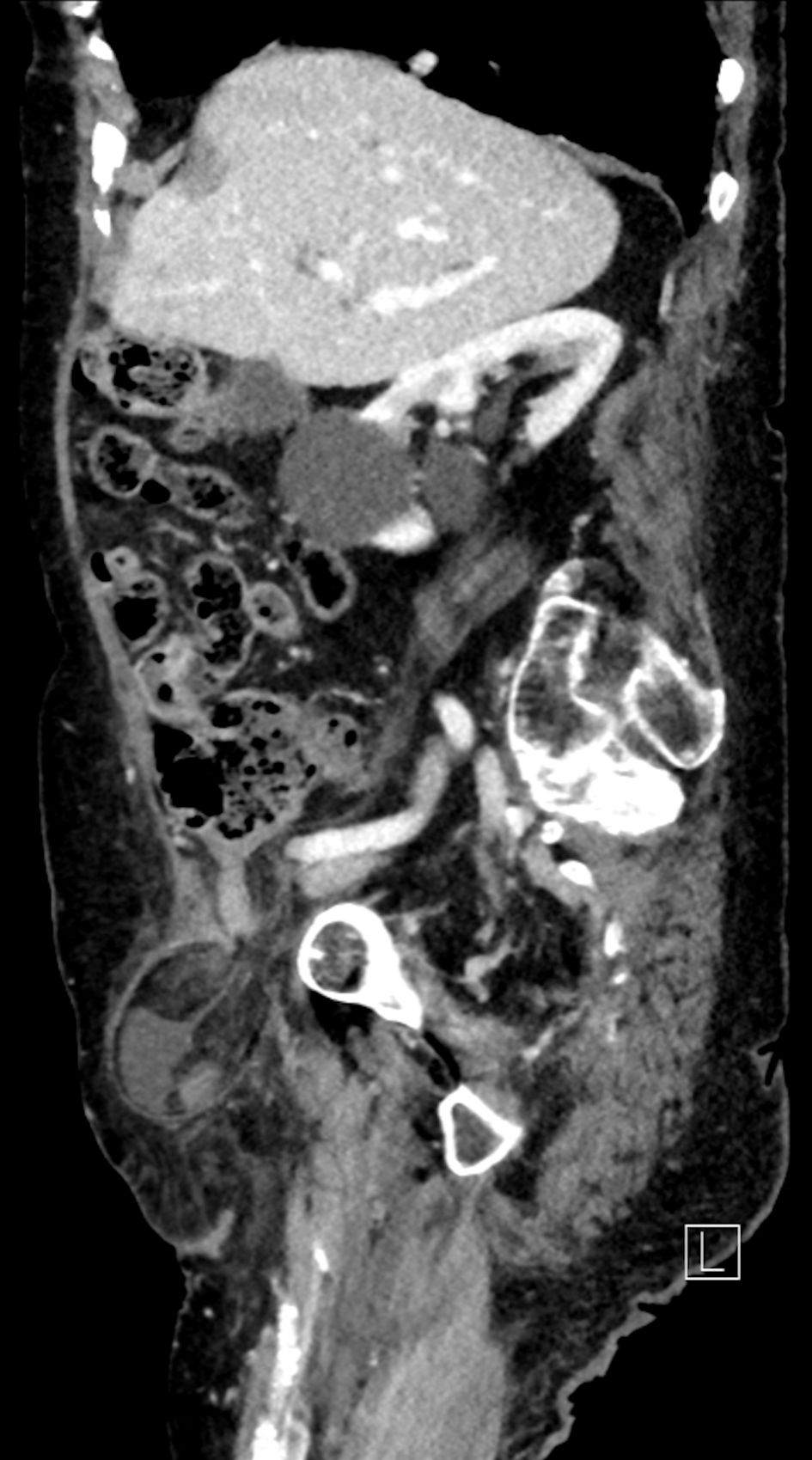 Click for large image | Figure 4. CT sagittal scan: right femoral hernia containing a bladder diverticulum. CT: computed tomography. |
Diagnosis
Right femoral hernia containing an inflamed cecal appendix and a bladder diverticulum was diagnosed.
Treatment
The patient underwent an urgent surgical procedure; and in consideration of the CT images, we decided to use a direct abdominal approach through a McBurney incision. An examination of the intra-abdominal area revealed a small amount of free fluid and healthy-looking intestinal loops. After the hernia was reduced, the presence of an inflamed appendix on its inside was confirmed, as well as a large bladder diverticulum with a diameter of 5 cm. An appendectomy was performed and the bladder diverticulum was separated from the hernial sac without any resectioning. The peritoneal sac was then closed, followed by the closure of peritoneal access. Finally, a posterior preperitoneal Nyhus closure was performed using a mesh of 75% resorbable poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) monofilament and a 25% polypropylene monofilament with a needle-free fixation.
Follow-up and outcomes
The patient was monitored for 24 h in the intensive care unit and was discharged after 7 days without any symptoms. At her 1-month and 3-month follow-up visits, the patient was fine and there were no signs of dehiscence or recurrence of the hernia. The patient was able to return to her normal daily life.
| Discussion | ▴Top |
De Garengeot’s hernia is an incarcerated femoral hernia containing the appendix which typically develops in women. A differential diagnosis would suggest an Amyand hernia, which is instead an inguinal hernia with appendicular content. In our case, the use of a CT scan made it possible to identify a complex de Garengeot’s hernia with appendicular and bladder content combined with concomitant acute appendicular inflammation.
Performing an abdominal CT scan with preoperative contrast media offered the advantage of being able to make a correct diagnosis and to plan a correct transabdominal, rather than inguino-crural, surgical approach.
The aim of our work is to highlight the importance of differential diagnosis in patients with a groin mass. There are currently no specific guidelines for the treatment of this type of hernia, as there is no statistical evidence on the best management approaches and their outcomes.
In order to better understand the surgical approach used in the treatment of this type of hernia and considering the small number of studies available, we decided to carry out a literature review by only selecting studies in English. The search terms used were: Garengeot, femoral hernia, appendicitis, diverticulum and bladder; and the literature search was performed on PubMed, EMBASE and the Cochrane Library [3-7]. Literature suggests that the most suitable imaging before proceeding with surgical treatment would be a CT scan of the abdomen, which is as an adequate diagnostic workup if the patient is stable. This ensures a prompt diagnosis and assists in therapeutic decision making. In addition, we examined the surgical techniques used: the current data are heterogeneous as the clinical presentation differs between cases and CT scans have not always been used prior to performing surgery. In literature there is a consensus on avoiding the use of mesh in cases of intestinal perforation or clear signs of infection.
In our opinion a surgical approach through inguinofemoral access using the McEvedy technique is the best way to treat non-septic appendicular hernias. In such cases the hernia can be repaired with the application of a mesh without antibiotic therapy and the positioning of drains.
On the other hand, if the hernial content shows possible signs of appendicitis, we believe that the surgical approach should follow McBurney’s transabdominal method, or in cases where there is a greater suspicion of infection, surgery should be performed through a lower paramedian incision. In the cases of perforation or clear signs of infection, it is recommended that the hernia is repaired only with a non-absorbable suture, avoiding the use of mesh. In this case postoperative antibiotic therapy may be prescribed and drains should be positioned only in the event of the spread of certain peritoneal sepsis.
Learning points
Some learning points from this case report include: 1) De Garengeot’s hernias are rare and can be confused with simple incarcerated femoral or inguinal hernias. If diagnosed correctly prior to surgery, the best surgical approach can be planned. 2) Currently, it is not possible to define a standard surgical approach for the treatment of de Garengeot’s hernias as there is no statistically significant data that defines the various outcomes based on the different types of surgery. We recommend a surgical approach through an inguinofemoral incision using the McEvedy technique in cases of non-septic appendicular hernia, whereas if the hernial content shows possible signs of appendicitis, we believe that the surgical approach should follow McBurney’s transabdominal method or that surgery should be performed through a lower paramedian incision. 3) In non-septic cases the hernia can be repaired with the application of a mesh. However, if there is any suspicion of sepsis, the repair is recommended only with a non-absorbable suture. 4) Postoperative antibiotic therapy should be prescribed only in the case of suspected infection, while we recommend the placement of drainages only in the case of the spread of certain intraperitoneal sepsis.
Acknowledgments
None to declare.
Financial Disclosure
The authors declared none specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflict of Interest
None to declare.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained.
Author Contributions
MDM: conception, planning and supervision of the paper. AT: acquisition of data and writer. LO: surgeon and clinical management of the case. LR: surgeon and clinical management of the case.
Data Availability
Any inquiries regarding supporting data availability of this study should be directed to the corresponding author.
| References | ▴Top |
- Amyand C. Of an inguinal rupture, with a pin in the appendix coeci, incrusted with stone, and some observations on wounds in the guts. Philosophical Transactions. 1835;39:1735-1736.
doi - de Garengeot RJC. Traite des operations de chirurgie, 2nd edn. Huart, Paris. 1731:369-371.
- Linder S, Linder G, Mansson C. Treatment of de Garengeot's hernia: a meta-analysis. Hernia. 2019;23(1):131-141.
doi pubmed - Bidarmaghz B, Borrowdale RC, Raufian K. A rare presentation of appendicitis inside the femoral canal: case report and literature review. Surg Case Rep. 2018;4(1):143.
doi pubmed - Fousekis FS, Christou PA, Gkogkos S, Aggeli P, Pappas-Gogos G. A case of De Garengeot's hernia with acute appendicitis and literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2018;49:55-57.
doi pubmed - Misiakos EP, Paspala A, Prodromidou A, Machairas N, Domi V, Koliakos N, Karatzas T, et al. De Garengeot's hernia: report of a rare surgical emergency and review of the literature. Front Surg. 2018;5:12.
doi pubmed - Bustamante Recuenco C, Garcia-Quijada Garcia J, Cendrero Martin M, Carabias Hernandez A, Serantes Gomez A, Sanz Munoz P, Delgado Millan MA, et al. De Garengeot's hernia: Case report and literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2019;64:58-61.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Current Surgery is published by Elmer Press Inc.
